- Home
- Product
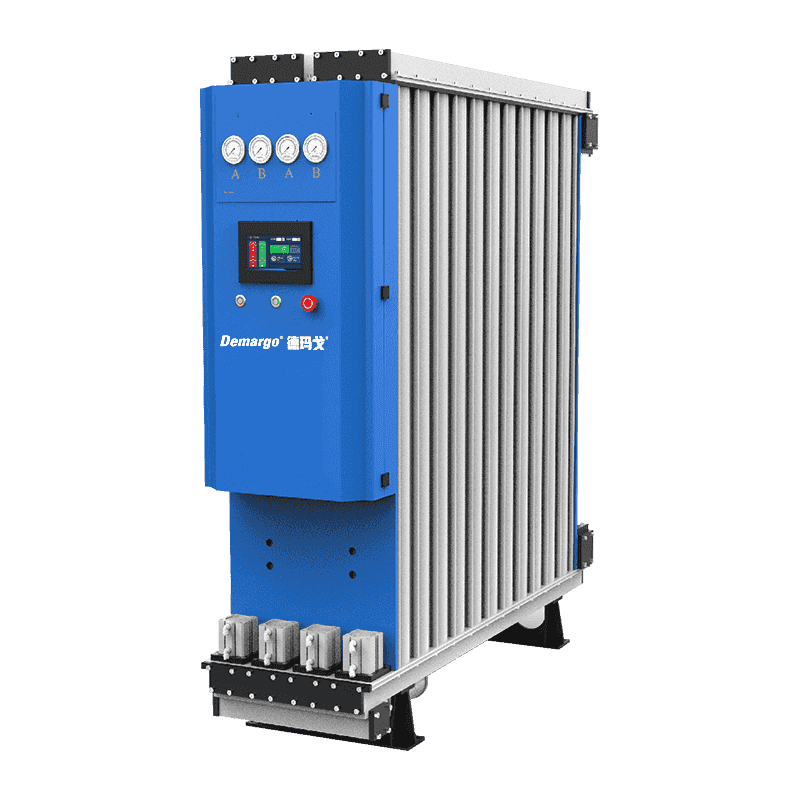
- Refrigerated Air Dryer
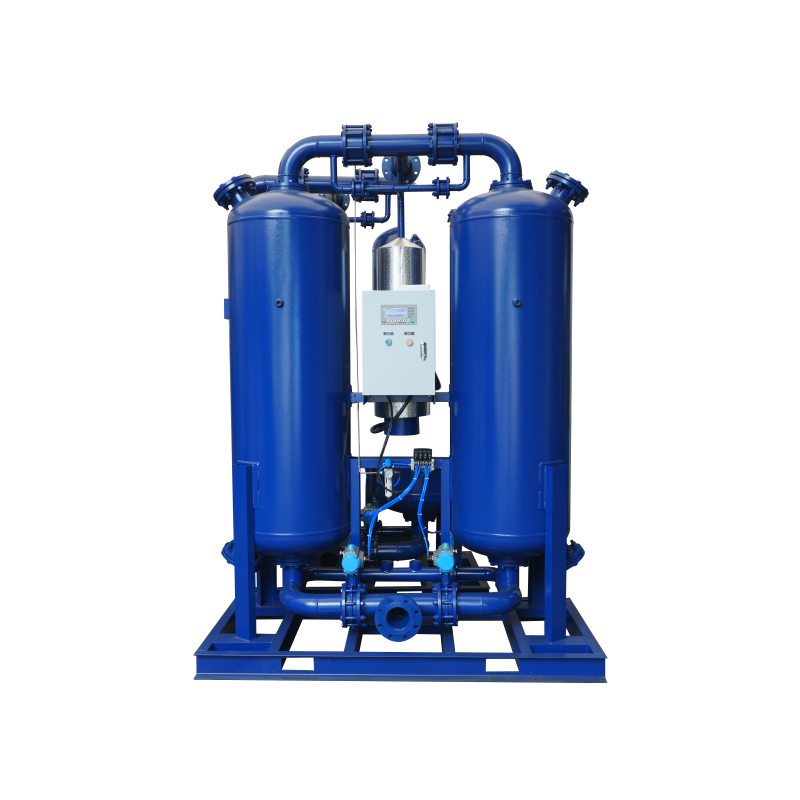
- Adsorption Dryer (Double Tower Type)
- Combined Low Dew Point Compressed Air Dryer
- Compression Heat Regeneration Adsorption Dryer
- Micro Air Consumption, Zero Air Consumption Blast Heat Regeneration Dryer
- Module/Mold Core Dryer
- Special Gas Dryer
- Compressed Air Filter
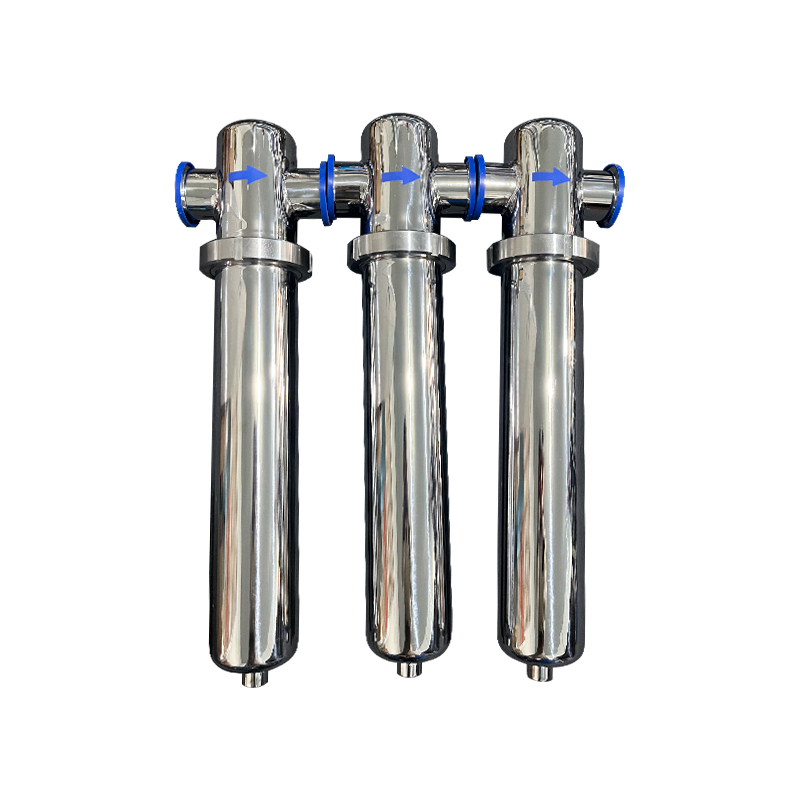
- Stainless Steel Compressed Air Filter
- High Efficiency Oil Remover
- Waste Oil Collector/Condensate/Condensate Treatment Separator
- Oil Water Separator
- Drainage Type
- Explosion-Proof Dryer
- About
- Application
- Case
- Support
- News
- Contact
INQUIRE NOW